Introduction
Since the dawn of existence, humans have encountered ever-changing environments. Their curiosity about the world around them has driven a keen interest in understanding and elucidating the occurrences in their surroundings. Engaging in experiments and observations has been a means to satisfy this curiosity and accumulate knowledge. Over the decades, this pursuit has guided numerous global research initiatives, necessitating the organization and systematization of the acquired knowledge for the benefit of humanity.
This organized knowledge is known as science, encompassing the systematic understanding gained through observations and experimentation. Science, owing to its extensive scope and diverse subjects, has evolved into various branches. Among these, chemistry stands out as one of the most consequential fields. Chemistry can be defined as the scientific domain dedicated to the study of matter, including its properties, composition, and the transformations it undergoes due to various activities. Numerous specialized branches within chemistry have emerged, each delving into specific disciplines of research.
Table of Content.
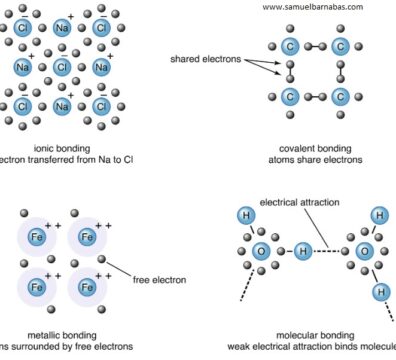
Chemistry, as a subdiscipline of science, involves the examination of matter and its constituent substances. It encompasses the investigation of substance properties and the transformations they undergo to produce new substances. Central to chemistry are the exploration of atoms, ions, and molecules, which collectively form elements and compounds. The interactions between these chemical entities are mediated by chemical bonds. Notably, the field of chemistry also delves into the study of interactions between matter and energy.
The exploration of properties, compositions, structures of elements and compounds, along with their transformative processes and the associated energy changes, constitutes the focal point of the scientific discipline known as chemistry.
The Connection Between Chemistry and Other Scientific Disciplines
The term ‘science’ encompasses the systematic exploration of the natural universe, its structure, and all its components. Given the vastness of the natural universe, science has been categorized into various disciplines, each addressing specific aspects of the universe. These disciplines can be grouped into three primary subcategories:
1. The Formal Sciences: These encompass the study of language-related disciplines that pertain to formal systems. Examples of scientific disciplines falling within this category are logic and mathematics, often considered as the “language of science.”
2. The Natural Sciences: This category involves the investigation of natural phenomena through experiments and observations. Chemistry, physics, and biology are included in this branch of science.
3. The Social Sciences: This category focuses on the study of human societies and the relationships among individuals within these societies. Examples of scientific disciplines falling under this category include psychology, sociology, and economics.
Branches of Chemistry
The five primary branches of chemistry are physical chemistry, organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, analytical chemistry, and biochemistry. Follow the buttons provided below to learn more about each individual branch.
In addition to these primary branches, numerous specialized fields within chemistry address interdisciplinary concerns. Examples of such fields include medicinal chemistry, neurochemistry, materials chemistry, nuclear chemistry, environmental chemistry, polymer chemistry, and thermochemistry.
Examples of Chemistry in Everyday Life
Chemical reactions are continually occurring in our surroundings, with the human body facilitating thousands of them daily. From the digestion of food to muscle movements, all bodily functions involve chemical reactions. Several instances of chemistry in the daily lives of humans are highlighted below.
1. Photosynthesis, the process enabling plants to convert water, sunlight, and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen, is a fundamental chemical reaction forming the basis of the entire food chain.
2. Soaps and detergents, crucial for hygiene, operate through a chemical process called emulsification. Additionally, they are produced using the chemical process known as saponification.
3. Sunscreen, used to shield against harmful UV-A and UV-B radiation from the sun, relies on chemistry. These lotions and creams consist of a blend of inorganic and organic compounds that either filter or block incoming ultraviolet radiation.
For further insights into the significance of chemistry in everyday life, follow the provided link.
Free Chemistry Study Material
The chemistry section hosts over 1000 chemistry articles for students to use as free study resources. Links to each of these articles have been sorted under their parent concepts and can be found in the collapsible tables provided below.
- Acids, Bases, and Salts
- Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids
- Amines
- Analytical Chemistry
- Atoms and Molecules
- Biomolecules
- Carbon and its Compounds
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemical Compounds
- Chemical Kinetics
- Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- Coal and Petroleum
- Combustion and Flame
- Electrochemistry
- Elements of the Periodic Table
- Environmental Chemistry
- Equilibrium
- Fibre to Fabric
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Hydrocarbons
- Hydrogen
- Named Reactions
- Organic Chemistry
- Periodic Classification of Elements
- Physical and Chemical Changes
- Pollution of Air and Water
- Polymers
- Redox Reactions
- Solutions
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- States of Matter
- Structure of Atom
- Surface Chemistry
- Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- The d and f – Block Elements
- The p-Block Elements
- The s Block Elements
- The Solid State
- Thermodynamics
- Uses of Chemical Compounds
Tutor's Column

Samuel Barnabas
TutorPeter Rose
ManagerGerald Gilbert
DeveloperCarolina
DeveloperLatest Post
- BARNABAS SAMUEL
- 12 March 2024
Chemical Formula Of
Chemical Formula Of Common CompoundsThe chemical formula of a compound is a symbolic representation of its chemical composition. Chemical formulae provide insight into the elements
- BARNABAS SAMUEL
- 08 March 2024
Chemical Bonding and
What Is Chemical Bonding?Chemical bonding refers to the formation of a chemical bond between two or more atoms, molecules or ions to give rise to a
- BARNABAS SAMUEL
- 08 March 2024
Carbon and its
What are Carbon and its Compounds?The molecules of a carbon compound must contain an atom of carbon. All living things, including plants and animals, are
- BARNABAS SAMUEL
- 26 February 2024
Test for Carboxyl
Carboxylic acids are highly versatile organic compounds known for their excellent physical and chemical properties. Their chemical structure consists of a carbonyl functional group and
- BARNABAS SAMUEL
- 24 February 2024
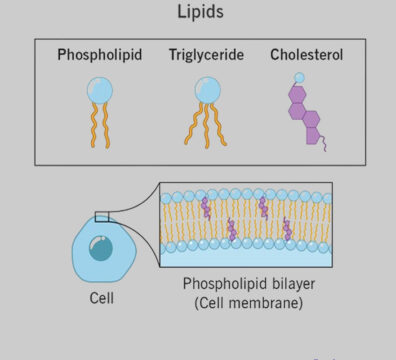
Lipids
Lipids Lipids Definition“Lipids are organic compounds that contain hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen atoms, which form the framework for the structure and function of living cells.”What