
Carboxylic acids are highly versatile organic compounds known for their excellent physical and chemical properties. Their chemical structure consists of a carbonyl functional group and a hydroxyl group, enabling easy interaction with polar compounds and involvement in many significant chemical reactions. Carboxylic acids are recognized as the most important functional group containing C=O.
Aim:
To identify the presence of carboxylic functional group in a given organic compound.
Theory:
Carboxylic acids exhibit a propensity to donate protons, functioning as acids. This characteristic proves beneficial in pinpointing the presence of the -COOH group.
The carboxylic functional group can be identified through any of the following tests:
- Litmus test
- Sodium bicarbonate test (or Sodium hydrogen carbonate test)
- Ester test
- Fluorescein test
(a) Litmus Test:
The carboxylic acid turns blue litmus red due to the acidity of the hydroxyl group present in -COOH, which is more acidic than in alcohol.
The chemical reaction can be represented as:
R-COOH + H2O → R-COO– + H3O+
Note: If the blue litmus paper changes color to red, then a carboxylic group is present. Phenol also gives this test.
(b) Sodium Bicarbonate Test:
When carboxylic acid reacts with sodium bicarbonate solution, carbon dioxide is evolved with a brisk effervescence, and sodium acetate is formed.
The chemical reaction can be represented as:
RCOOH + NaHCO3 → RCOONa + H2O + CO2↑ (brisk effervescence)
Note: This test is used to distinguish between carboxylic acid from phenol. Phenol does not give this test.
(c) Ester Test:
Carboxylic acid reacts with alcohol in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid and forms a pleasant smelling ester. This reaction is known as esterification.
The chemical reaction is given below.
RCOOH + R-OH + H2SO4 → RCOO-R (Ester) + H2O
Note: Formation of a sweet smelling compound indicates the presence of carboxylic group in the given organic compound.
(d) Fluorescein Test:
This test is given by dicarboxylic acid. Dicarboxylic acid on heating gives acid anhydride. When this anhydride is treated with resorcinol in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid a fluorescent
dye is formed and so this reaction is called fluorescein test.
The chemical reaction is given below.
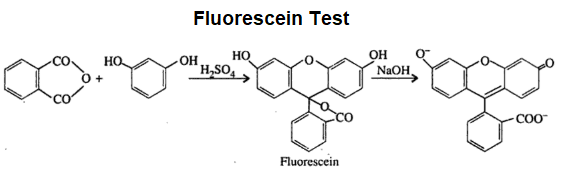
Note: This test should be performed only if the compound gives positive results in litmus test and sodium bicarbonate test.
Materials Required:
- Blue litmus paper
- Sodium bicarbonate (or) sodium hydrogen carbonate
- Ethyl alcohol
- Concentrated sulphuric acid
- Resorcinol
- Acid anhydride
- Given organic compound
- Test tubes
- Test tube holders
- Beaker
- Glass rod
- Stirrer
Procedure:
(a) Litmus Test:
- Add a drop of given organic compound on blue litmus paper.
- Observe the colour change in blue litmus paper.
- If the colour of blue litmus changes to red the presence of carboxylic acid.
Note: Blue litmus solution is also used in the place of blue litmus paper.
(b) Sodium Bicarbonate Test:
- Prepare a saturated solution of sodium bicarbonate by dissolving sodium bicarbonate in 1ml of water.
- Add the given organic compound to the saturated solution of sodium bicarbonate solution.
- Shake the solution well.
- If there is an evolution of brisk effervescence then it indicates the presence of carboxylic acid.
Note: Use acid free alcohol for the test.
(c) Ester Test:
- Mix the given compound with ethyl alcohol and concentrated sulphuric acid.
- Heat the mixture in a dry test tube in a water bath.
- Pour the reaction mixture into a beaker carefully containing water.
- Neutralise the excess sulphuric acid.
- If a sweet smelling substance is sensed then it indicates the presence of acid.
(d) Fluorescein Test:
- Take the given organic compound to be tested in a test tube.
- Mix with 100mg of resorcinol and 0.5ml of concentrated sulphhuric acid.
- Heat the test tube gently on a bunsen burner.
- Pour the mixture into a beaker containing dilute sodium hydroxide solution.
- Appearance of green colour fluorescent solution indicates the presence of carboxylic acid group.
Note: The resultant solution should be alkaline
Observations:
| Litmus test | Carboxylic group turns blue litmus red. |
| Sodium bicarbonate test | Brisk effervescence indicates the presence of a carboxylic acid |
| Ester test | Formation of a sweet smelling compound indicates the presence of carboxylic group. |
| Fluorescein test | Appearance of green colour fluorescent solution indicates the presence of acid group. |
Results and Discussion:
The given organic compound is ___________ .
Precautions:
- In sodium bicarbonate test use acid free alcohol so that it should not interfere with the functional group of the given organic compound.
- The addition of sodium bicarbonate should be carried out slowly so that the effervescence is visible clearly.
- Dicarboxylic acids like oxalic acid, terephthalic acid and isophthalic acid do not give fluorescein test.
