What is an Amino acid?
“Amino Acids are the organic compounds that combine to form proteins, hence they are referred to as the building components of proteins. These biomolecules are involved in several biological and chemical functions in the human body and are the necessary ingredients for the growth and development of human beings. There are about 300 amino acids that occur in nature.”
Amino acids comprise essential amino groups (-NH2) and carboxyl groups (-COOH). These vital building blocks constitute the core elements of proteins. Peptides and proteins alike consist of extensive sequences of these amino acids, totaling a distinct set of twenty crucial constituents responsible for the intricate construction of proteins.
List of 20 Amino acids with the chemical formula
Listed below are the names of twenty amino acids along with their chemical formula.
| Alanine | C3H7NO2 | Leucine | C6H13NO2 |
| Aspartic Acid | C4H7NO4 | Lysine | C6H14N2O2 |
| Asparagine | C4H8N2O3 | Methionine | C5H11NO2S |
| Arginine | C6H14N4O2 | Proline | C5H9NO2 |
| Cytosine | C4H5N3O | Phenylalanine | C9H11NO2 |
| Cysteine | C3H7NO2S | Serine | C3H7NO3 |
| Glycine | C2H5NO2 | Tyrosine | C9H11NO3 |
| Glutamine | C5H10N2O3 | Threonine | C4H9NO3 |
| Histidine | C6H9N3O2 | Tryptophan | C11H12N2O2 |
| Isoleucine | C6H13NO2 | Valine | C5H11NO2 |
General properties of Amino acids
– Amino acids have very high melting and boiling points.
– They appear as white crystalline solid substances.
– In terms of taste, some amino acids are sweet, others are tasteless, and a few are bitter.
– Most amino acids are soluble in water but insoluble in organic solvents.
Essential and Non-essential Amino acids
“Within the spectrum of 20 amino acids, our bodies possess the capability to synthesize a select few independently, termed as non-essential amino acids. This category encompasses alanine, asparagine, arginine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, cysteine, glutamine, proline, glycine, serine, and tyrosine.
In contrast, there exist nine amino acids deemed essential, as our bodies lack the capacity to produce them internally. These indispensable elements include isoleucine, histidine, lysine, leucine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, methionine, threonine, and valine.”
Also read about Proteins
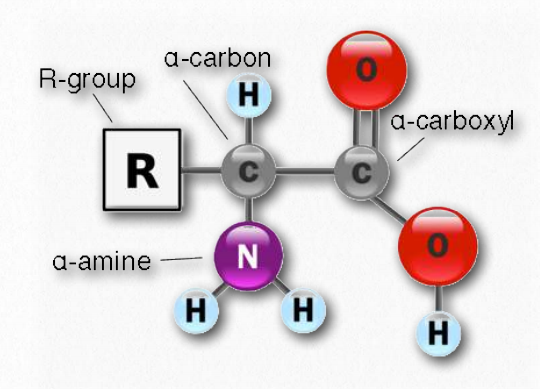
Structure of Amino acids
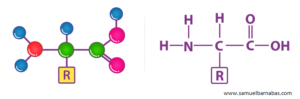
The general structure of Amino acids is H2NCH RCOOH.
“The 20 naturally occurring amino acids share fundamental structural traits, each possessing an amino group (-NH3+), a carboxylate (-COO-) group, and a hydrogen atom bonded to the same carbon atom. Their distinctiveness lies in their side-chain, known as the R group, which varies from one amino acid to another. At the α-carbon, every amino acid bears four distinct groups:
1. Amino group
2. COOH
3. Hydrogen atom
4. Sidechain (R)”
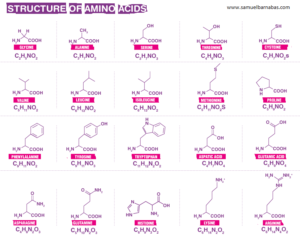
Structure of 20 Amino acids with their chemical formula
The structure of twenty amino acids with their chemical formula are shown below.
Sources of Amino acids

Amino acids serve vital roles in various biological and chemical functions throughout the body, encompassing tissue building and repair, enzyme formation and activity, food digestion, and molecular transport, among others. While our bodies can synthesize certain amino acids, those deemed essential must be obtained from protein-rich foods in our daily diet.
Foods abundant in amino acids encompass a wide array of plant-based options such as broccoli, beans, beetroots, pumpkin, cabbage, nuts, dried fruits, chia seeds, oats, peas, carrots, cucumber, green leafy vegetables, onions, soybeans, whole grains, peanuts, legumes, and lentils. Fruits also contribute to amino acid intake with options like apples, bananas, berries, figs, grapes, melons, oranges, papaya, pineapple, and pomegranates. Animal-derived sources include dairy products, eggs, seafood, chicken, beef, pork, and more.

Functions of Amino acids
- Functions of Essential Amino acids
- Phenylalanine helps in maintaining a healthy nervous system and in boosting memory power.
- Valine acts as an important component in promoting muscle growth.
- Threonine helps in promoting the functions of the immune system.
- Tryptophan is involved in the production of vitamin B3 and serotonin hormones. This serotonin hormone plays a vital role in maintaining our appetite, regulating sleep and boosting our moods.
- Isoleucine plays a vital role in the formation of haemoglobin, stimulating the pancreas to synthesize insulin, and transporting oxygen from the lungs to the various parts.
- Methionine is used in the treatment of kidney stones, maintaining healthy skin and also used in controlling invade of pathogenic bacteria.
- Leucine is involved in promoting protein synthesis and growth hormones.
- Lysine is necessary for promoting the formation of antibodies, hormones, and enzymes and in the development and fixation of calcium in bones.
- Histidine is involved in many enzymatic processes and in the synthesizing of both red blood cells (erythrocytes) and white blood cells (leukocytes).
- Functions of Non-Essential Amino acids
- Alanine functions by removing toxins from our body and in the production of glucose and other amino acids.
- Cysteine acts as an antioxidant and provides resistance to our body; it is important for making collagen. It affects the texture and elasticity of the skin
- Glutamine promotes a healthy brain function and is necessary for the synthesis of nucleic acids – DNA and RNA.
- Glycine is helpful in maintaining the proper cell growth, and its function, and it also plays a vital role in healing wounds. It acts as a neurotransmitter.
- Glutamic acid acts as a neurotransmitter and is mainly involved in the development and functioning of the human brain.
- Arginine helps in promoting the synthesis of proteins and hormones, detoxification in the kidneys, healing wounds, and maintaining a healthy immune system.
- Tyrosine plays a vital role in the production of the thyroid hormones -T3 and T4, in synthesizing a class of neurotransmitters and melanin, which are natural pigments found in our eyes, hair, and skin.
- Serine helps in promoting muscle growth and in the synthesis of immune system proteins.
- Asparagine is mainly involved in the transportation of nitrogen into our body cells, formations of purines and pyrimidine for the synthesis of DNA, the development of the nervous system and improving our body stamina.
- Aspartic acid plays a major role in metabolism and in promoting the synthesis of other amino acids.
- Proline is mainly involved in the repairing of the tissues in the formation of collagen, preventing the thickening and hardening of the walls of the arteries (arteriosclerosis) and in the regeneration of new skin.
- Functions of Essential Amino acids
Deficiency of Amino acids
“As highlighted earlier, amino acids serve as the foundational units of proteins, which in turn are integral to nearly all life processes. Thus, it is imperative to incorporate all nine essential amino acids into our daily diet to uphold the healthy and proper functioning of our bodies. Deficiencies in amino acids can lead to various pathological disorders, including:”
– Edema
– Anemia
– Insomnia
– Diarrhea
– Depression
– Hypoglycemia
– Loss of Appetite
– Fat deposit in the liver
– Skin and hair related problems
– Headache, weakness, irritability, and fatigue
.