Classification of Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Alcohol, phenol, and ether are classes of organic compounds that have extensive applications across various industries and in domestic settings.
- Alcohol is produced when a saturated carbon atom is linked to a hydroxyl (-OH) group.
- Phenol is generated by replacing a hydrogen atom in a benzene molecule with the -OH group.
- Ether is formed when an oxygen atom is bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups.
CLASSIFICATION OF ALCOHOL, PHENOL AND ETHER
In this section, we will discuss how alcohols, phenol’s and ethers are classified.
Classification of Alcohol
Based on the number of hydroxyl groups attached, alcohols can be categorized into three types:
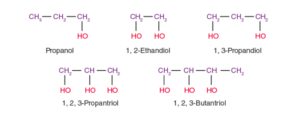
- Monohydric alcohols: These alcohols contain one -OH group. For example, CH3CH2-OH.
- Dihydric alcohols: These alcohols contain two -OH groups. For instance, 1,2-Ethanediol.
- Trihydric alcohols: These alcohols contain three -OH groups. An example is 1,2,3-Propanetriol.
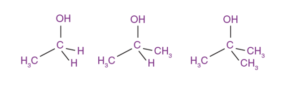
Alcohols can be classified into three types based on the number of carbon atoms directly attached to the carbon bonded with the -OH group.
- Primary alcohols: One carbon atom is directly attached.
- Secondary alcohols: Two carbon atoms are directly attached.
- Tertiary alcohols: Three carbon atoms are directly attached.
Classification of Phenol
Depending on the number of hydroxyl groups attached, phenols can be classified into three types.
- Monohydric phenols: They contain one -OH group.
- Dihydric phenols: They contain two -OH groups. They may be ortho-, meta- or para- derivative.
- Trihydric phenols: They contain three -OH groups.

Classification of Ether
Depending on the type of the alkyl or aryl groups attached to the oxygen atom in ether, it can be classified into two types.
- Symmetrical ether: Also known as the simple ether, the alkyl or the aryl group attached to either side of the oxygen atoms are the same. Examples are CH3OCH3, C2H5OC2H5, etc.
- Unsymmetrical ether: Also known as the mixed either, the alkyl or the aryl group attached to either side of the oxygen atoms, are not the same. Examples are CH3OC2H5, C2H5OC6H5, etc.